Mitosis illustration Biology Diagrams Clarify mitosis phases with our free lesson, ideal for student interaction, this activity fosters creative visualization of cell division at StoryboardThat.

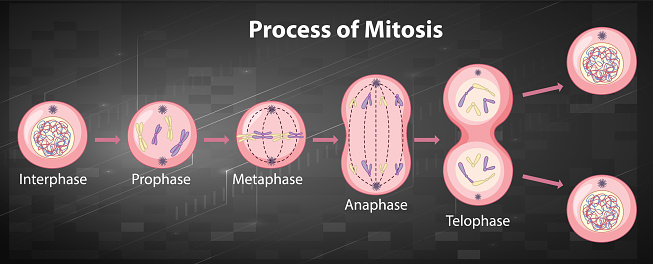
At the end of interphase, the cell has duplicated its chromosomes and is ready to move them into separate cells, called daughter cells. This occurs during the four steps of mitosis, called prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase. Check out what the mitosis phases look like under a microscope. Mitosis, the process by which a cell divides, consists of four distinct stages: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Drawing the stages of mitosis is an essential skill for students of biology, allowing them to visualize and understand the complex processes involved in cell division. The diagrams depict the changes in chromosome structure, spindle fiber formation, and nuclear membrane Explore the stages of mitosis with detailed diagrams. Understand each phase and discover real-world applications of this essential cell division process.
Mitosis: Cell Division Stages Illustrated Biology Diagrams
Learn about the stages of mitosis with a clear and detailed diagram. Discover the different phases of cell division, from prophase to telophase, and understand the important events that occur during each stage. This informative article provides a visual representation to help you understand the process of mitosis.

Curious about the stages of mitosis? Our complete guide goes deep on the 4 mitosis phases: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.

Stages of Mitosis (with pictures) Flashcards Biology Diagrams
A normal resting cell exists in a state called interphase in which the chromatin is undifferentiated in the heavily-stained nucleus, as illustrated above. Before the cell enters the mitosis phase, it first undergoes a synthesis or S phase where each chromosome is duplicated and consists of two sister chromatids joined together by a specific DNA These are the stages of Mitosis, including pictures, illustrations, and explanations of each stage, excluding cytokinesis.
