Modeling Mitosis How living things create new cells Biology Diagrams In vertebrates, initial condensation in prophase precedes condensin recruitment to the central axis, which may be interpreted as initially condensed states being stapled together by the association of condensin [32]. Chromosome condensation appears to be a multi-layered process with different mechanisms operating at different levels Prophase is defined by the onset of chromosome condensation and is actually the final part of G 2 phase. TADs disassemble inside the intact nucleus and mitotic chromosomes begin to form their characteristic array of loops (see Chapter 8). In the cytoplasm, a dramatic change in the dynamic properties of the microtubules decreases their half

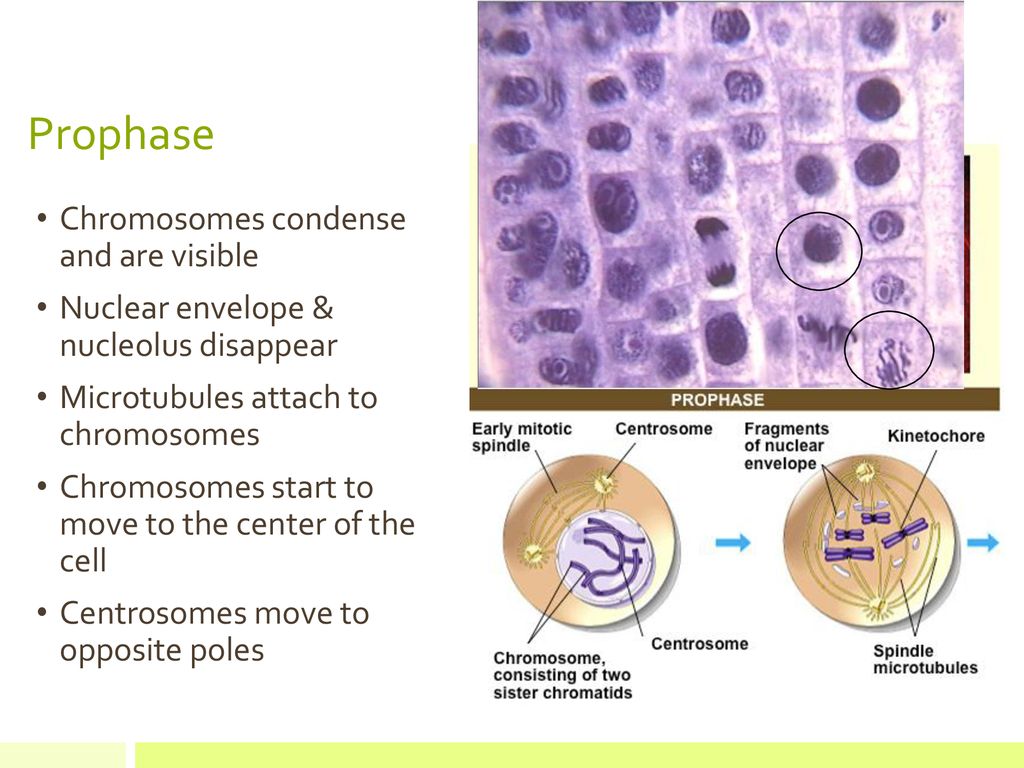
During preprophase, these mechanisms are set up. Like animals, the chromosomes condense and can be seen, and the nucleolus disappears during prophase. After prophase of mitosis, the chromosomes with will attached to microtubules, arranged in the middle of the cell, and the sister chromatids of every chromosome will be separated into new cells. During prophase, the replicated chromosomes (each consisting of two sister chromatids) condense and are recognizable under the microscope. Inhibitory phosphorylation of this protein promotes chromosome condensation. 11 Aurora B kinase is also responsible for phosphorylating and activating subunits of condensin. 12 When Aurora B is depleted,
+condenses+into+chromosomes..jpg)
Prophase - Definition and Stages in Mitosis and Meiosis Biology Diagrams
Phase 1: Prophase. Prophase is the first step of mitosis. This is when the genetic fibers within the cell's nucleus, known as chromatin, begin to condense and become tightly compacted together. During interphase, the parent cell's chromosomes are replicated, but they aren't yet visible. The process of chromosome condensation during prophase II is a marvel of cellular organization, driven by a series of highly regulated molecular events. Central to this process are condensin complexes, which play a pivotal role in structuring and compacting chromatin. These protein complexes, composed of multiple subunits, facilitate the
+Nuclear+membrane+disappears..jpg)
Chromosome Condensation. As prophase begins, one of the most visually striking events is the condensation of chromatin into distinct chromosomes. This transformation is facilitated by a group of proteins known as condensins, which play a pivotal role in compacting the long strands of DNA into tightly coiled structures. The condensation process In meiosis, prophase serves as the initial stage of the first of the two divisions. In this prophase (sometimes identified as prophase I), the homologous paternal and maternal chromosomes condense in the nucleus of the diploid cell. Each pair of chromosomes—called a tetrad, or a bivalent—consists of four chromatids. Prophase is the phase that follows the interphase and typically the first and longest phase in the cell cycle, for both mitosis and meiosis. Chromosome condensation forms two sister chromatids which are X-shaped and joined at a point known as a centromere. Image Source: Khan Academy.
Nested Irreducible Complexity Biology Diagrams
Chromosome Condensation. Chromosome condensation is a crucial part of cell division. It happens during the prophase stage. This process ensures genetic material is organized and ready for distribution to daughter cells. The following sections will explore how chromosome condensation occurs and why it is vital for genetic material organization.
